Page 950 - Plastic Process Equipment, Inc
P. 950
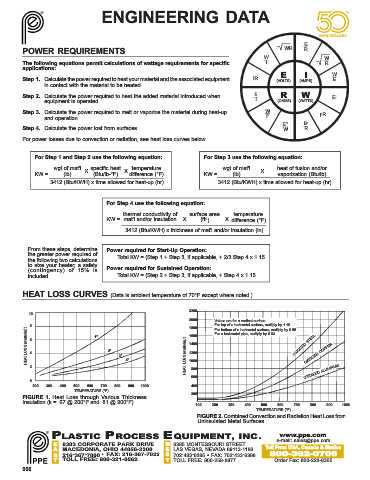
ENGINEERING DATA
E
POWER REQUIREMENTS WR R
W W
The following equations permit calculations of wattage requirements for specific I R
applications:
E I W
Step 1. Calculate the power required to heat your material and the associated equipment IR (VOLTS) (AMPS) E
in contact with the material to be heated.
Step 2. Calculate the power required to heat the added material introduced when E R W EI
equipment is operated. I (OHMS) (WATTS)
Step 3. Calculate the power required to melt or vaporize the material during heat-up W I R
2
and operation. I 2
E 2 E 2
Step 4. Calculate the power lost from surfaces. W R
For power losses due to convection or radiation, see heat loss curves below.
For Step 1 and Step 2 use the following equation: For Step 3 use the following equation:
wgt of mat'l X specific heat X temperature wgt of mat'l X heat of fusion and/or
KW = (lb) (Btu/lb-°F) difference (°F) KW = (lb) vaporization (Btu/lb)
3412 (Btu/KWH) x time allowed for heat-up (hr) 3412 (Btu/KWH) x time allowed for heat-up (hr)
For Step 4 use the following equation:
thermal conductivity of surface area temperature
2
KW = mat'l and/or insulation X (ft ) X difference (°F)
3412 (Btu/KWH) x thickness of mat'l and/or insulation (in)
From these steps, determine Power required for Start-Up Operation:
the greater power required of
the following two calculations Total KW = (Step 1 + Step 3, if applicable, + 2/3 Step 4 x 1.15
to size your heater; a safety
(contingency) of 15% is Power required for Sustained Operation:
included. Total KW = (Step 2 + Step 3, if applicable, + Step 4 x 1.15
HEAT LOSS CURVES (Data is ambient temperature of 70°F except where noted.)
2200
10
2000 Values are for a vertical surface.
8 1800 For top of a horizontal surface, multiply by 1.10.
HEAT LOSS (watts/in. 2 ) 6 4 1" 2" 3" HEAT LOSS (watts/in. 2 ) 1400 OXIDIZED STEEL
For bottom of a horizontal surface, multiply by 0.55.
For a horizontal pipe, multiply by 0.83.
1600
OXIDIZED COPPER
1200
2 4" 1000 OXIDIZED ALUMINUM
800
600
0
200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 400
TEMPERATURE (°F)
200
FIGURE 1. Heat Loss through Various Thickness
Insulation (k = .67 @ 200°F and .81 @ 900°F)
100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
TEMPERATURE (°F)
FIGURE 2. Combined Convection and Radiation Heat Loss from
Uninsulated Metal Surfaces.
PLASTIC PROCESS EQUIPMENT, INC. www.ppe.com
e-mail: sales@ppe.com
E 8303 CORPORATE PARK DRIVE W 6385 MONTESSOURI STREET
A MACEDONIA, OHIO 44056-2300 E LAS VEGAS, NEVADA 89113-1186 Toll Free: USA, Canada & Mexico
S 216-367-7000 • FAX: 216-367-7022 S 702-433-6385 • FAX: 702-433-6388 800-362-0706
T TOLL FREE: 800-321-0562 T TOLL FREE: 800-258-8877 Order Fax: 800-223-8305
950